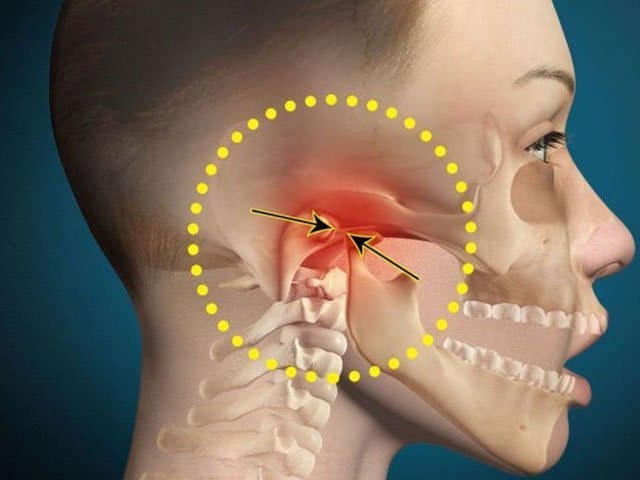
Jaw discomfort can be more than just an occasional annoyance—it may be a sign of a deeper problem involving the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). When this joint becomes strained or dysfunctional, it can lead to a condition known as Temporomandibular Joint Disorder, or TMD. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain, stiffness, and difficulty in performing everyday activities like speaking, eating, and yawning. Understanding what TMD is, why it occurs, and how it can be treated is essential to finding relief and maintaining overall oral health.
What Is TMD?
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) acts as the hinge that connects your jawbone to your skull, allowing smooth movement when you open and close your mouth. When this joint or its surrounding muscles experience inflammation, strain, or misalignment, the condition is referred to as Tmd. TMD can manifest in a variety of ways, ranging from mild stiffness to severe pain and jaw locking. While it often affects adults, anyone who experiences frequent jaw tension or grinding may develop symptoms.
TMD can be temporary for some, resolving on its own with rest or lifestyle changes. However, chronic cases may require professional diagnosis and treatment to prevent further discomfort or damage to the joint.
Common Causes of TMD
TMD does not have a single cause—it is typically the result of multiple factors that affect the joint and muscles controlling jaw movement. Some of the most common causes include:
- Teeth Grinding (Bruxism): Habitual clenching or grinding, often during sleep, places excessive pressure on the jaw joint.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can cause people to unconsciously tense their facial and jaw muscles.
- Injury or Trauma: Physical injury to the jaw, head, or neck can disrupt the joint’s alignment.
- Misaligned Bite: Uneven bite patterns may cause strain on one side of the jaw more than the other.
- Arthritis: Inflammatory joint conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the TMJ.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or forward head posture can lead to jaw misalignment and muscle strain.
Recognizing the Symptoms of TMD
TMD symptoms can vary widely in severity and may even mimic other health issues, making diagnosis challenging. Common signs include:
- Persistent jaw pain or tenderness
- Clicking, popping, or grinding sounds when opening or closing the mouth
- Difficulty opening the mouth fully or jaw locking
- Facial pain or tension around the cheeks and temples
- Headaches, earaches, or ringing in the ears
- Stiffness in the neck and shoulders
- Uneven bite or discomfort while chewing
If you experience several of these symptoms consistently, it’s best to seek professional advice for a proper evaluation.
How TMD Is Diagnosed
Diagnosing TMD involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests. A healthcare provider may:
- Examine jaw movement and listen for clicking or popping sounds.
- Check for tenderness in the facial muscles and joint area.
- Evaluate bite alignment and range of motion.
- Order imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to view the structure of the joint.
This thorough assessment helps determine whether the symptoms stem from joint inflammation, muscle tension, or another related cause.
Treatment Options for TMD
The good news is that most TMD cases can be managed with non-invasive treatments. The right approach depends on the cause and severity of symptoms. Here are some common treatment methods:
1. Home Remedies and Self-Care
For mild cases, self-care can significantly reduce discomfort:
- Apply warm compresses to relax tight jaw muscles.
- Eat soft foods to minimize strain while chewing.
- Avoid extreme jaw movements such as wide yawning or gum chewing.
- Practice relaxation techniques to reduce stress-related clenching.
2. Physical Therapy
Therapeutic exercises help strengthen the jaw muscles and improve mobility. A physical therapist may guide you through gentle stretching and relaxation techniques to relieve muscle tension.
3. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help manage inflammation. In more severe cases, doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants or anti-anxiety medications to ease tension.
4. Mouthguards or Splints
Custom-fitted dental appliances prevent teeth grinding during sleep and reduce pressure on the TMJ. They also help in aligning the jaw correctly.
5. Injections or Minimally Invasive Treatments
For chronic pain or inflammation, joint injections—such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid—may provide relief. These procedures are usually quick and done in a clinical setting.
6. Surgical Interventions
Surgery is typically the last resort and only recommended when all other treatments fail. Procedures may involve arthroscopy, joint repair, or joint replacement in severe cases.
Managing TMD Through Lifestyle Changes
Beyond medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments play a significant role in managing TMD:
- Reduce Stress: Meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises can help prevent muscle tightening.
- Maintain Good Posture: Keep your head aligned with your spine to reduce jaw strain.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports muscle and joint function.
- Avoid Hard Foods: Cut food into smaller pieces to reduce the load on your jaw.
- Regular Exercise: Gentle neck and shoulder stretches can ease overall tension.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Ignoring TMD symptoms can lead to chronic pain or even permanent joint damage. Early intervention not only prevents complications but also improves the chances of full recovery. People who seek timely treatment often experience significant improvement within weeks.
Long-Term Outlook
While TMD can be uncomfortable, it is usually manageable with consistent care and healthy habits. Many individuals recover fully once they identify and address the root cause. For those with chronic symptoms, long-term management through therapy and relaxation techniques can help maintain comfort and functionality.
Final Thoughts
TMD is a complex but treatable condition that affects both physical comfort and quality of life. Understanding its causes, recognizing early signs, and adopting appropriate treatments are key to recovery. By combining self-care, professional guidance, and preventive practices, you can restore jaw function and live free from ongoing pain and stiffness. Early awareness and consistent management remain the best strategies for keeping your jaw healthy and pain-free.